DuckDB Connector Configuration#
DuckDB supports integration with various cloud storage providers through secrets for secure access to your data.
Storage Providers
The following storage services are supported for retrieving and storing data:
- Azure Blob Storage: Use Microsoft's cloud storage.
- AWS S3: Connect to Amazon Simple Storage Service.
- Cloudflare R2: Leverage Cloudflare’s distributed storage.
- Google Cloud Storage: Access Google’s cloud-based object storage.
- Postgres: Connect directly to a PostgreSQL database.
By supporting these formats and providers, DuckDB ensures flexibility and compatibility with a wide range of data environments, enabling powerful data analysis and management capabilities.
To setup your Duck Connector:
- Name: Enter a name for the connector to identify it within your app.
- Data Source Slug: Create a unique identifier for the connector to reference it within the app.
- Description (Optional): Provide a brief description to explain the connector's purpose or details. This helps you manage multiple connectors.
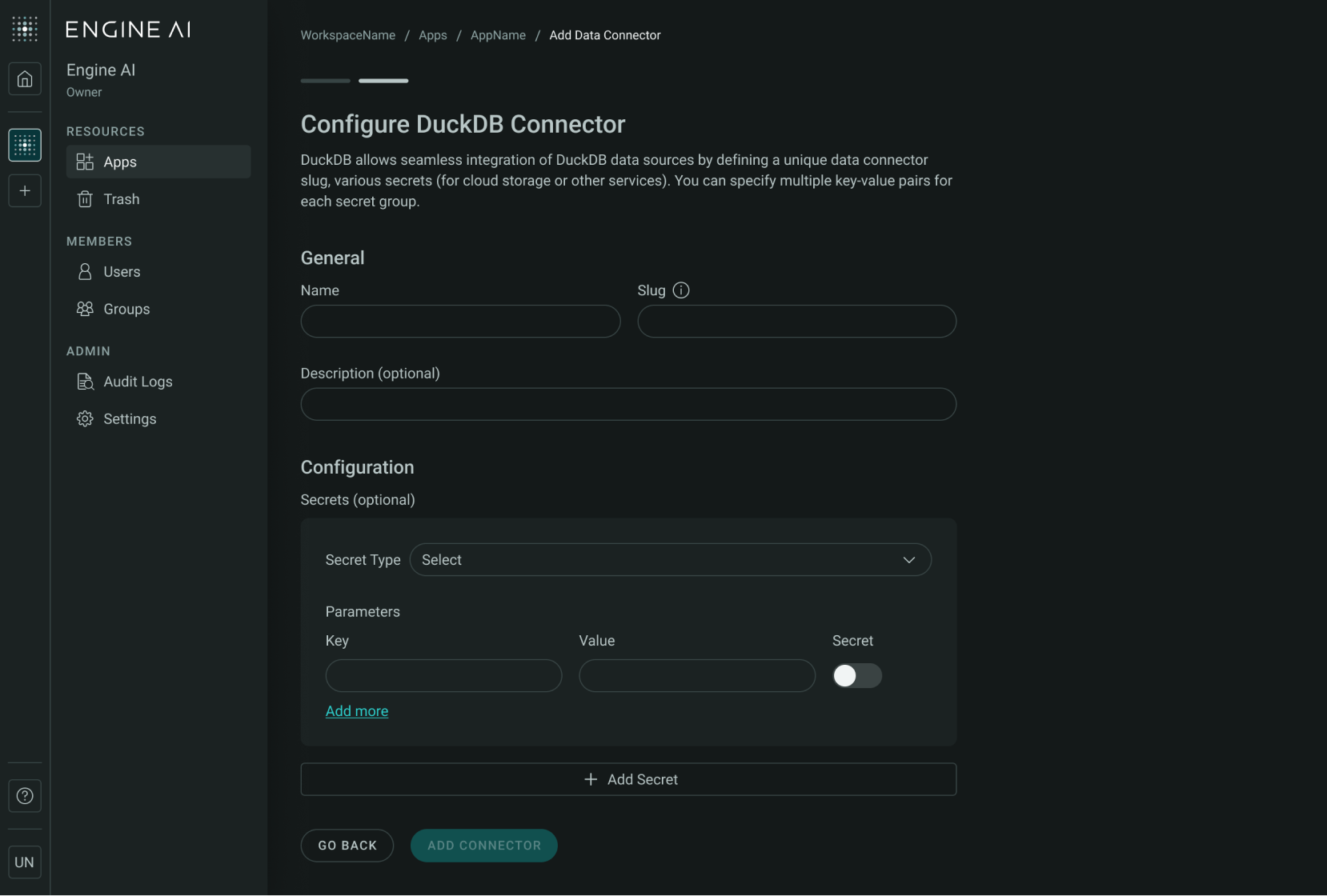
Configuration:You have to select secret type and set up configuration key-value parameters.
- Secret Slug: A unique identifier of the secret.
- Secret Type: Select the appropriate type of secret based on your integration or authentication requirements.
- Key-value Parameters: Define the required parameters as key-value pairs. Each secret may include multiple parameters necessary for successful authentication or configuration.
Note
You can associate multiple secrets with a single connector. To reference a specific secret, use its unique slug within your setup.
Testing Connection#
The DuckDB connector allows you to connect to various data sources using a SQL-like interface. To test your connection, you’ll need to write a query that uses the correct syntax based on the type of external source you’ve connected to. DuckDB supports connections to:
- PostgreSQL
- MySQL
- Azure Blob Storage
- Amazon S3
- Google Cloud Storage (GCS)
When you click “Test Connection”, you’ll be prompted to enter a query that uses a specific slug depending on your data source type.
Testing Instructions:
- Identify which source you’re connecting to (Postgres, MySQL, Azure, S3, or GCS).
- Use the correct slug syntax and query format.
- Enter a valid query in the test modal and click “Run Test”.
- If successful, you’ll see a confirmation message. If not, an error message will guide you to fix your query.
Query Format by Source Type#
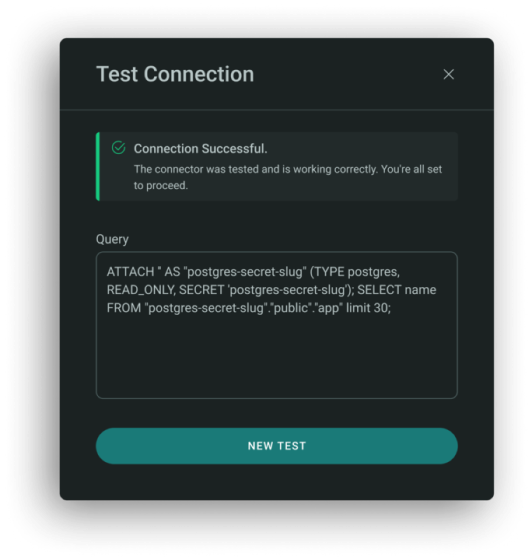
Postgres
To test a Postgres, use the following syntax to attach the database and run your query:
Example:
ATTACH '' AS "postgres-secret-slug" (TYPE postgres, READ_ONLY, SECRET 'postgres-secret-slug');
SELECT name FROM "postgres-secret-slug"."public"."app" limit 30;
What to Enter:
- Use postgres-secret-slug as the alias for your secret slug.
- Schema and table names (e.g., "public"."app") must match your source structure.
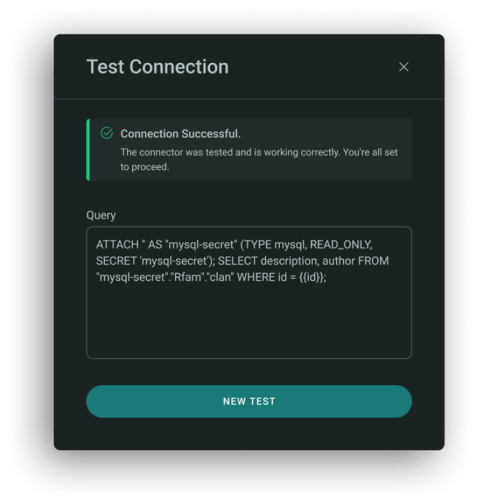
MySQL
To test connection to MySQL, use the following syntax to attach the database and run your SQL query:
Example:
ATTACH '' AS "mysql-secret" (TYPE mysql, READ_ONLY, SECRET 'mysql-secret');
SELECT description, author FROM "mysql-secret"."Rfam"."clan" WHERE id = {{ id }};
What to Enter:
- Use mysql-secret as the alias for your secret slug.
- Replace {{ id }} with a real condition to retrieve data from your table.
- Schema/table references (e.g., "Rfam"."clan") must match your database.
Azure Blob Storage
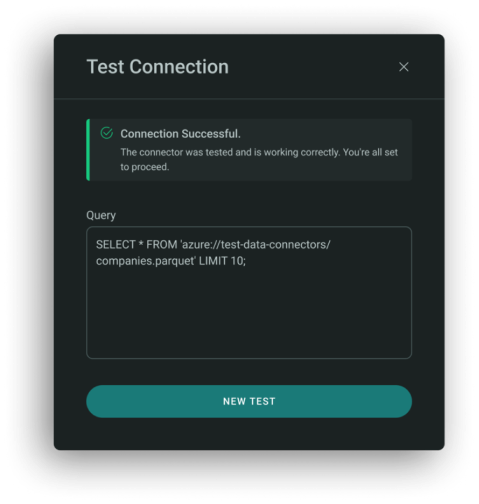
To test connection to Azure Blob Storage and read from a .parquet file run the query:
Example:
SELECT * FROM 'azure://test-data-connectors/companies.parquet' LIMIT 10;
What to Enter:
- The file path should reflect your Azure container and blob location.
- You can adjust LIMIT to retrieve a smaller/larger sample.
- Ensure the file is accessible and your credentials are correctly configured.
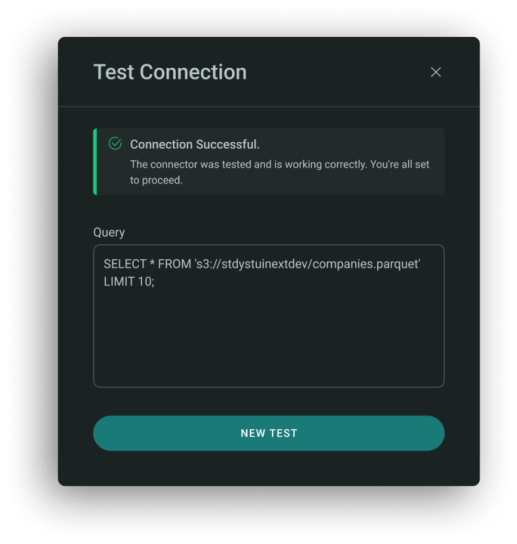
Amazon S3
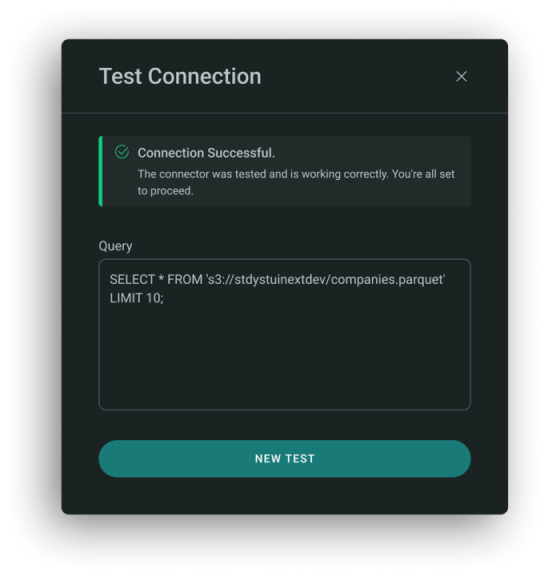
To test connection to S3 and read from a .parquet file run the query:
Example:
SELECT * FROM 's3://stdystuinextdev/companies.parquet' LIMIT 10;
What to Enter:
- Provide the S3 URI to your file.
- You can add LIMIT as needed for testing.
- Ensure your access credentials and permissions are properly set up.
Google Cloud Storage (GCS)
To test connection and access data from GCS run the query:
Example:
SELECT * FROM 'gs://your-bucket-name/path/to/file.parquet' LIMIT 10;
What to Enter:
- Update the path to your actual GCS file location.
- Like other storage connectors, ensure access permissions are valid.